GSTPAM News Bulletin August 2023
President’s MessageAdv. Pravin Shinde President – GSTPAM |
|
Dear Esteemed Members,
As a President of the Goods and Services Tax Practitioners’ Association of Maharashtra let me thank and express my sincere gratitude once again to all of you for reposing trust and confidence in me and bestowing the honour of being the President of this august Association. I express my sincere gratitude to all of you for unanimously and unopposed electing me as President of this esteemed association “GSTPAM”
It is with great pleasure we are presenting our first GSTPAM News Bulletin’s for 2023-2024. The News Bulletin has been always been channel to communicate with members about Association forthcoming events and activities and also about latest development in the GST MVAT & Allied laws Updates. Now a day we have covered various Articles on Income Tax Updates, Income Tax Circular and Notification, Investment Plan, Summary of Recent Cases under GST, DGFT & Customs Updates, Charitable Trust Updates and Updates on Finance etc. I am thankful to all the contributors for the same.
The Inaugural Study Circle Meeting was conducted on 01st August 2023 on the topic of “Highlights on 50th GST Council Meeting” by CA Sujata Rangnekar and it was really a pleasant experience to hear her interpretations and views on the topic. At the outset, I place on record my sincere gratitude to the Honorable President of Maharashtra Sales Tax Tribunal, Shri Suhas Mane and Tribunal members for inaugurating 1st Study Circle meeting with their gracious hands and blessing to all of us. In the said event GSTPAM and STTBA jointly felicitated our senior member Adv. Shri P. C Joshi in appreciation of his relentless services to the profession for last sixty one years.
The Know your Managing committee meeting is schedule on 9th August 2023.
The Non-Residential Refresher Course (NRRC) is scheduled on 21st and 22nd August 2023 at Shirdi. I would request to enroll for the same. Details are available on our website.
This time Our Coaching Class Committee has decided to start Virtual Coaching class on GST Topics in Marathi as well as in Gujarathi languages and same should be start in 1st week of September 2023 itself. I request all the members to enroll yourself as well as your office staff for the same and take the benefit.
This Year our Chairman Shri Pradip Kapadia and Convenors Shri Aloke Singh and Shri Ashish Ruparelia have decided to celebrate member’s birthday and marriage anniversary and dates should be reported in News Bulletin on the basis of whatever members database available with our record.
This is an e-bulletin and is being sent by e-mail to all the members of association and all trade industries and associate tax associations. It is also available after login in the Publications menu on the Home page of our Website www.gstpam.org. All the details of meetings and seminars will be uploaded on website and the same can be viewed on YouTube and GSTPAM Facebook page also.
So Happy viewing and Happy reading.
Thank you all,
Jai Hind, Jai Maharashtra, Jai Bharat!
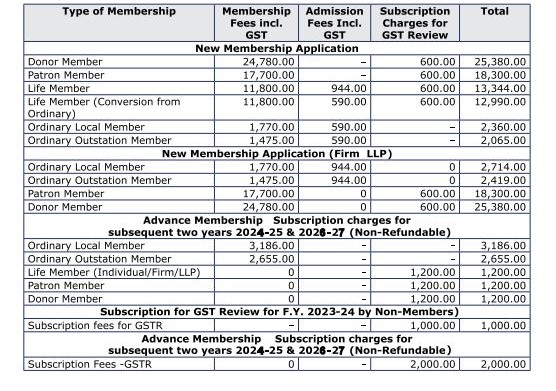
CIRCULAR FOR RENEWAL OF MEMBERSHIP/SUBSCRIPTION CHARGES FOR THE F.Y. 2023-24
Dear Members,
RENEWAL OF MEMBERSHIP FOR F.Y. 2023-24
The Membership Fees for the year 2023-24 are due for renewal on 01.04.2023. We appreciate your Continuing support and participation in the activities of our Association.
The timely Renewal of Membership will enable the members to continuously receive the updates on various activities of GSTPAM along with the GST Review, News Bulletin, Circulars, Messages, Webinars and online access to the website www.gstpam.org. The Life Members only need to renew the subscription charges for the GST Review. The members can also avail the benefit of discount by paying advance for subsequent two years membership fees /subscription charges.
The Membership Renewal Fees received after 30th April, 2023 will be subject to approval of the Managing Committee. If the Renewal fees for a particular year are not paid, then the member is liable to pay Admission Fees again for Renewal in the subsequent year.
Delayed Renewal Members will be provided Pre Renewal GST Review subject to availability upon payment of such additional courier charges.
The details of Membership Subscription Fees are given below for your ready reference:



GST, MVAT & ALLIED LAW UPDATESCompiled by Adv. Pravin Shinde |
|
|
Notification under Central Tax |
||
| Notification No. | Date of Issue | Subject |
| 18/2023-Central Tax | 17/07/2023 | Seeks to extend the due date for furnishing FORM GSTR-1 for April, May and June, 2023 for registered persons whose principal place of business is in the State of Manipur |
| 19/2023- Central Tax | 17/07/2023 | Seeks to extend the due date for furnishing FORM GSTR-3B for April, May and June, 2023 for registered persons whose principal place of business is in the State of Manipur |
| 20/2023- Central Tax | 17/07/2023 | Seeks to extend the due date for furnishing FORM GSTR-3B for quarter ending June, 2023 for registered persons whose principal place of business is in the State of Manipur |
| 21/2023- Central Tax | 17/07/2023 | Seeks to extend the due date for furnishing FORM GSTR-7 for April, May and June, 2023 for registered persons whose principal place of business is in the State of Manipur |
| 22/2023- Central Tax | 17/07/2023 | Seeks to extend amnesty for GSTR-4 non-filers |
| 23/2023- Central Tax | 17/07/2023 | Seeks to extend time limit for application for revocation of cancellation of registration |
| 25/2023- Central Tax | 17/07/2023 | Seeks to extend amnesty for GSTR-9 non-filers |
| 26/2023- Central Tax | 17/07/2023 | Seeks to extend amnesty for GSTR-10 non-filers |
| 27/2023- Central Tax | 31/07/2023 | Seeks to notify the provisions of section 123 of the Finance Act, 2021 (13 of 2021). |
| 28/2023- Central Tax | 31/07/2023 | Seeks to notify the provisions of sections 137 to 162 of the Finance Act, 2023 (8 of 2023). |
| 29/2023- Central Tax | 31/07/2023 | Seeks to notify special procedure to be followed by a registered person pursuant to the directions of the Hon’ble Supreme Court in the case of Union of India v/s Filco Trade Centre Pvt. Ltd., SLP(C) No.32709- 32710/2018. |
| 30/2023- Central Tax | 31/07/2023 | Seeks to notify special procedure to be followed by a registered person engaged in manufacturing of certain goods. |
| 31/2023- Central Tax | 31/07/2023 | Seeks to amend Notification No. 27/2022 dated 26.12.2022 |
| 32/2023- Central Tax | 31/07/2023 | Seeks to exempt the registered person whose aggregate turnover in the financial year 2022-23 is up to two crore rupees,from filing annual return for the said financial year |
| 33/2023-Central Tax | 31/07/2023 | Seeks to notify “Account Aggregator” as the systems with which information may be shared by the common portal under section 158A of the CGST Act, 2017. |
| 34/2023- Central Tax | 31/07/2023 | Seeks to waive the requirement of mandatory registration under section 24(ix) of CGST Act for person supplying goods through ECOs, subject to certain conditions. |
| 35/2023- Central Tax | 31/07/2023 | Seeks to appoint common adjudicating authority in respect of show cause notices in favour of against M/s BSH Household Appliances Manufacturing Pvt Ltd. |
| 36/2023- Central Tax | 17/07/2023 | Seeks to notify special procedure to be followed by the electronic commerce operators in respect of supplies of goods through them by composition taxpayers. |
| 37/2023- Central Tax | 31/07/2023 | Seeks to notify special procedure to be followed by the electronic commerce operators in respect of supplies of goods through them by unregistered persons |
| 37/2023- Central Tax | 31/07/2023 | Seeks to notify special procedure to be followed by the electronic commerce operators in respect of supplies of goods through them by unregistered persons |
| 38/2023- Central Tax | 31/07/2023 | Seeks to make amendments (Second Amendment , 2023) to the CGST Rules, 2017. |
|
Notification under Central Tax (Rate) |
||
| Notification No | Date of Issue | Subject |
| 06/2023- Central Tax (Rate) | 26/07/2023 | Seeks to amend notification No. 11/2017- Central Tax (Rate) so as to notify change in GST with regards to services as recommended by GST Council in its 50th meeting held on 11.07.2023. |
| 07/2023- Central Tax (Rate) | 26/07/2023 | Seeks to amend notification No. 12/2017- Central Tax (Rate) so as to notify change in GST with regards to services as recommended by GST Council in its 50th meeting held on 11.07.2023. |
| 08/2023- Central Tax (Rate) | 26/07/2023 | Seeks to amend notification No. 13/2017- Central Tax (Rate) so as to notify change in GST with regards to services as recommended by GST Council in its 50th meeting held on 11.07.2023. |
| 09/2023- Central Tax (Rate) | 26/07/2023 | Seeks to amend No. 01/2017- Central Tax (Rate) to implement the decisions of 50th GST Council. |
| 10/2023-Central Tax (Rate) | 26/07/2023 | Seeks to amend No. 26/2018- Central Tax (Rate) to implement the decisions of 50th GST Council |
| Corrigendum | 31/07/2023 | Corrigendum to notification no. 10/2023 Central Tax (Rate) |
|
Notification under Integrated Tax (Rate) |
||
| Notification No | Date of Issue | Subject |
| 01/2023- Integrated Tax | 31/07/2023 | Seeks to notify all goods or services which may be exported on payment of integrated tax and on which the supplier of such goods or services may claim the refund of tax so paid. |
|
Notification under Integrated Tax (Rate) |
||
| Notification No | Date of Issue | Subject |
| 06/2023- Integrated Tax (Rate) | 26/07/2023 | Seeks to amend notification No. 08/2017- Integrated Tax (Rate) so as to notify change in GST with regards to services as recommended by GST Council in its 50th meeting held on 11.07.2023 |
| 07/2023- Integrated Tax (Rate) | 26/07/2023 | Seeks to amend notification No. 09/2017- Integrated Tax (Rate) so as to notify change in GST with regards to services as recommended by GST Council in its 50th meeting held on 11.07.2023. |
| 08/2023- Integrated Tax (Rate) | 26/07/2023 | Seeks to amend notification No. 10/2017- Integrated Tax (Rate) so as to notify change in GST with regards to services as recommended by GST Council in its 50th meeting held on 11.07.2023. |
| 09/2023- Integrated Tax (Rate) | 26/07/2023 | Seeks to amend No. 01/2017- Integrated Tax (Rate) to implement the decisions of 50th GST Council. |
| 10/2023- Integrated Tax (Rate) | 26/07/2023 | Seeks to amend No. 27/2018- Integrated Tax(Rate) to implement the decisions of 50th GST Council. |
| Corrigendum | 31.07.2023 | Corrigendum to notification no. 10/2023 Integrated Tax (Rate) |
|
Notification under Union Territory Tax (Rate) |
||
| Notification No | Date of Issue | Subject |
| 06/2023-Union Territory Tax (Rate) | 26/07/2023 | Seeks to amend notification No. 11/2017- Union Territory Tax (Rate) so as to notify change in GST with regards to services as recommended by GST Council in its 50th meeting held on 11.07.2023. |
| 07/2023 -Union Territory Tax (Rate) | 26/07/2023 | Seeks to amend notification No. 12/2017- Union Territory Tax (Rate) so as to notify change in GST with regards to services as recommended by GST Council in its 50th meeting held on 11.07.2023. |
| 08/2023- Union Territory Tax (Rate) | 26/07/2023 | Seeks to amend notification No. 13/2017- Union Territory Tax (Rate) so as to notify change in GST with regards to services as recommended by GST Council in its 50th meeting held on 11.07.2023. |
| 09/2023-Union Territory Tax (Rate) | 26/07/2023 | Seeks to amend No. 01/2017- Union Territory Tax (Rate) to implement the decisions of 50th GST Council. |
| 10/2023-Union Territory Tax (Rate) | 31.07.2023 | Seeks to amend No. 26/2018- Union Territory Tax (Rate) to implement the decisions of 50th GST Council. |
| Corrigendum | 31.07.2023 | Corrigendum to notification no. 10/2023 Union Territory Tax (Rate) |
|
Notification under Compensation Cess (Rate) |
||
| Notification No | Date of Issue | Subject |
| 03/2023-Compensation Cess (Rate) | 26/07/2023 | Seeks to amend No. 1/2017- Compensation Cess(Rate) to implement the decisions of 50th GST Council |
|
Circular under CGST Act |
||
| Circular No | Date of Issue | Subject |
| 192/04/2023-GST | 17/07/2023 | Clarification on charging of interest under section 50(3) of the CGST Act, 2017, in cases of wrong availment of IGST credit and reversal thereof. |
| 193/05/2023-GST | 17/07/2023 | Clarification to deal with difference in Input Tax Credit (ITC) availed in FORM GSTR-3B as compared to that detailed in FORM GSTR-2A for the period 01.04.2019 to 31.12.2021 |
| 194/06/2023-GST | 17/07/2023 | Clarification on TCS liability under Sec 52 of the CGST Act, 2017 in case of multiple E-commerce Operators in one transaction |
| 195/07/2023-GST | 17/07/2023 | Clarification on availability of ITC in respect of warranty replacement of parts and repair services during warranty period |
| 196/08/2023-GST | 17/07/2023 | Clarification on taxability of share capital held in subsidiary company by the parent company |
| 197/09/2023-GST | 17/07/2023 | Clarification on refund-related issues |
| 198/10/2023-GST | 17/07/2023 | Clarification on issue pertaining to e-invoice |
| 199/11/2023-GST | 17/07/2023 | Clarification regarding taxability of services provided by an office of an organisation in one State to the office of that organisation in another State, both being distinct persons |
| 200/12/2023-GST | 01/08/2023 | Clarification regarding GST rates and classification of certain goods based on the recommendations of the GST Council in its 50th meeting held on 11th July, 2023 |
| 201/13/2023-GST | 01/08/2023 | Clarifications regarding applicability of GST on certain services |
|
Trade Circular MVAT Act 2005 |
||
| Notification / Circular No | Date of Issue | Subject |
| 11T of 2023 | 26/07/2023 | Settelment of Arrears of Tax, Interest and Penalty or Late Fees under various acts administered by MGST Department.ation Cess(Rate) to implement the decisions of 50th GST Council |
| SUMMARY OF RECENT CASES UNDER GST
Compiled by CA Aditya Surte |
|
- Settlement of mutual debts through book adjustment by netting-off of receivables of one GSTIN by another GSTIN of same company, or net-off of receivables with payables of supplier of goods/service, is valid payment of consideration for inward supplies; it satisfies second proviso to Section 16(2) of CGST Act, 2017 and input tax credit is admissible subject to other prescribed conditions and restrictions.(Kerala Authority for Advance Rulings in Advance Ruling No. KER/12/2021, decided on 03/04/2023 in the case of Malabar Gold Pvt. Ltd.)
- Where the Applicant intends to establish a gurukul style school, offering subjects such as Sanskrit, English, Indian classical music and dance, Kalaripayattu, and Yoga as any normal schools but with difference that subjects taught here are not same, since there is no advancement of religious, spirituality or yoga said services do not qualify as charitable activities, making them ineligible for tax exemption. Further, where the Applicant is neither providing pre-school education nor education up to higher secondary school and they are following their own curriculum, applicant is not covered under definition of “educational institution” as per Notification No. 9/2017-Integrated Tax (Rate) and, thus, cannot claim exemption as per Sl. No. 69 of the said notification. (Karnataka Advance Ruling Authority in Advance Ruling No. KAR ADRG 23/2023, decided on 13/07/2023 in the case of Isha Foundation)
- Where the Applicant is providing boarding and lodging facilities and also ancillary services to inhabitants referring the service as ‘paying guest accommodation / hostel’, however, the accommodation provided to inhabitant is not a residential dwelling but a room where un-related people share the room and invoices are raised per bed on monthly basis, the services are akin to guest house and lodging services and cannot be termed as ‘residential dwelling’. Thus, PG/hostel rent paid by inhabitants does not qualify for exemption under Sl. No. 12 of Notification No. 12/2017-Cental Tax (Rate), dated 28/06/2017 as services provided by applicant are not akin to renting of residential dwelling for use as residence.Ancillary services such as meals, fully furnished rooms, washing machine facility, vehicle parking facility, etc. are optional facilities / separate services, hence, cannot be naturally bundled services with the Applicant’s main supply of hostel / accommodation service.Applicant is providing boarding and lodging facilities and ancillary services to inhabitants by taking residential accommodation on rent. GST under reverse charge will be applicable on rental paid to landowners by the Applicant.
(Karnataka Advance Ruling Authority in Advance Ruling No. KAR ADRG 25/2023, decided on 13/07/2023 in the case of Srisai Luxurious Stay LLP)
INCOME TAX UPDATESCompiled By By Adv. Ajay Talreja |
|
Preparing for ITR Filing for Salaried Individuals: Key Precautions & Checks
A Comprehensive Guide: Precautions for Salaried Individuals Filing ITR Filing Income Tax Returns (ITR) is a task that requires careful attention. Salaried individuals especially need to keep certain crucial points in mind while preparing their ITR. This comprehensive guide elucidates these essential aspects.
- Identifying the Correct ITR Form Determining the right ITR form for your tax situation is the first step. For the Assessment Year (AY) 2023-24, ITR – 1 or Sahaj, is for resident individuals with a total income that includes: Salary or pension income Income from one house property (excluding cases where loss is brought forward from previous years) Income from other sources (excluding lottery winnings and income from racehorses) Agricultural income up to Rs 5000 On the other hand,ITR-2 is for individuals or Hindu Undivided Families (HUF) whose total income comprises: Salary or pension income Income from multiple properties Income from other sources including lottery winnings and income from racehorses Individuals holding directorship in a company Investments in unlisted equity shares at any time during the financial year Being a resident not ordinarily resident (RNOR) and non-resident Income from capital gains Foreign income or assets Agricultural income exceeding Rs 5,000.
- Reviewing Form 16 Thoroughly Form 16 is a TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) certificate that your employer issues detailing your salary income and tax deducted. Ensure that you compare the salary and deductions mentioned in Form 16 with Form 26AS and your proofs. Also, check deductions like interest on self-occupied house property and 80CCD(1B) NPS, which you may not have submitted to the employer but can still claim.
- Incorporating All Other Incomes Be sure to account for all other income like bank interest, fixed deposit interest, capital gains, rental income, and income from shares. Cross-verify and ensure that all of these income sources are duly reflected in your ITR.
- Downloading and Checking Form 26AS, AIS, and TIS Form 26AS is your tax credit statement, which shows the tax that has been deducted from your income and deposited with the government by your deductor. AIS (Annual Information Statement) and TIS (Tax Information Statement) contain additional information about your financial transactions. You should cross-check whether all entries in these forms are accounted for in your ITR. Remember, if a particular income is mentioned in these forms but doesn’t belong to you, you can ignore it. At the same time, even if some income is not reflected in these forms, it must be reported in your ITR.
- Validating All Deductions Ensure that all deductions are checked carefully against the proofs you have. In some cases, your deductions may not appear in Form 16, leading to excess tax deduction. In such instances, you can claim these deductions while filing your ITR. Importantly, avoid reporting any false deductions that you did not make during the financial year.
- Choosing Between the New and Old Tax Regime The Indian government introduced a new optional tax regime in Budget 2020. Under this, individuals can opt for lower tax rates on the condition of forgoing certain exemptions and deductions available under the old regime. It’s crucial to compare the tax liabilities under both regimes and select the one beneficial for you.
- Avoiding Hastened Filing One common mistake people make is filing their ITR in a hurry. Such haste can lead to errors, which might result in wrong filing or notices from the Income Tax Department. Therefore, always take your time to prepare your ITR and consult a tax professional if you have any queries. In conclusion, keeping these precautions in mind can help you file your ITR accurately and smoothly. Remember, paying taxes is not just about compliance; it’s also about contributing to the nation’s development. So, do it right!
B. Amendments w.e.f. Finance Act 2023.
When Income Tax Return f i l ing is Compulsory irrespective of their income level? Criteria of deposits made in current accounts: If during the F.Y., any person has deposited (cash and other deposits) more than Rs. 1 Crore in his current account(s) in the bank(s) or co-operative bank(s), the person is required to file a return of income, even if his total income is below the basic exemption limit of 2,50,000/-.
Criteria of expenses on foreign travel: If a person has spent more than Rs. 2 Lakh on Foreign Travel during the F.Y. for himself/herself or for somebody else, the person is required to file a return of income, even if his total income is below the basic exemption limit of 2,50,000/-.
Criteria of Expenses on electricity consumption: If a person has incurred expenses of more than Rs. 1 lac in the F.Y. towards the Electricity Bill(s), the person is required to file a return of income, even if his total income is below the basic exemption limit of 2,50,000/-. Criteria of Turnover in business: If a person has any business and total sale, turnover or gross receipts in the business is more than 60 Lakh for the F.Y., the person is required to file a return of income, even if his total income is below the basic exemption limit of 2,50,000/-.
Criteria of Professional receipts: If a person is a professional and his total professional receipts for the F.Y. is more than 10 Lakh, the person is required to file a return of income, even if his total income is below the basic exemption limit of 2,50,000/-.
Criteria of TDS/TCS: An Individual person, whose aggregate tax deducted at source (TDS) or tax collected at source (TCS) during F.Y. is Rs 25,000 or more, has to file an income tax return even if his total income is below the basic exemption limit of 2,50,000/-. In the case of senior citizens, the aggregate TDS or TCS amount making them to file a return of income is Rs 50,000 or more.
Criteria of deposits in savings bank account: If a person has total deposits (including cash and other deposits) in his saving bank account(s) of more than 50 Lakh in the F.Y., he has to file income tax return even if his total income is below the basic exemption limit of 2,50,000/-.
Before concluding, I would like to say that- It is advisable to file the return of income, irrespective of your income level. Because the return of income is a very important document and it is helpful in many areas, say, VISA processing where foreign embassies sometimes require evidence of return of income for three years, obtaining bank loans, etc. Please note that filing of return of income is also required for making a claim for a refund of income tax.
If a person has incurred a loss in any F.Y. under the head “ Profits and gains of business or profession” or under the head “ Capital Gains”, he must file the return of loss on or before the due date, otherwise, he will not be entitled to claim to carry forward of the loss under these heads in the next year for adjustment of the said loss against income of the next year.
The NRIs, who derive income in India from any sources of Income, must file a return of Income in India.
Addition in bogus purchase transaction reduced on pro-rata basis
Ravi Kedia Vs ITO (ITAT Raipur)
Accordingly, on the basis of my aforesaid observations the matter is restored to the file of the A.O. ITAT Raipur held that addition in case of bogus purchase transaction restricted to the extent of the difference between the gross profit of genuine purchases transactions and gross profit of bogus purchases transactions. Facts- On the basis of information that had surfaced in the course of survey action u/s. 133A of the Act conducted at the business premises of five rice millers a/w. two brokers on 15.03.2016, it was gathered by the A.O that the assessee as a beneficiary had procured bogus purchase bills of a value of Rs.30,12,000/- during the year under consideration from two parties. Assessee submitted that he had already surrendered 10% of the purchases under the IDS, 2016. It was observed by the A.O that the disclosure made by the assessee under IDS, 2016 on account of bogus purchases in itself established that he had not made genuine purchases from the aforementioned parties. Apart from that, it was observed by the A.O that the disclosure of Rs.2,73,200/- that was made by the assessee worked out at 9% (approx.) of the total amount of bogus billing of Rs.30.12 lac. A.O after deliberating at length on the modus-oparandi that was adopted by the rice millers/brokers for procuring bogus purchase bills etc., concluded that the assessee had not made any genuine purchases from the parties in question. Accordingly, A.O disallowed 25% of the value of bogus purchases and made a consequential addition of Rs.7,53,000/-. Aggrieved the assessee carried the matter in appeal before the CIT(Appeals) but without success. Conclusion- Held that would be worked out by the A.O as regards the profit which the assessee would have made by procuring the goods in question at a discounted value from the open/grey market, as against the value booked in his books of accounts, i.e by restricting the addition to the extent of the difference between the gross profit of genuine purchases transactions and gross profit of bogus purchases transactions would be reduced on a pro-rata basis, i.e to the extent such gross profit is attributable to bogus/unverified purchase transactions vis-à-vis total purchases made during the year.
Section 40(a)(ia) of Income Tax Not Applicable in Case of Short Deduction of TDS
Advait Agrotech Private Limited Vs PCIT (ITAT Ahmedabad)
Introduction: In the case of Advait Agrotech Pvt. Ltd. Vs PCIT, the Income Tax Appellate Tribunal (ITAT) Ahmedabad recently ruled that the provisions of section 40(a)(ia) of the Income Tax Act cannot be invoked in the event of short deduction of TDS (Tax Deducted at Source). This pivotal ruling came after Advait Agrotech Pvt. Ltd. challenged the assessment order passed by the Principal Commissioner of Income Tax (PCIT) under section 263 of the Income Tax Act.
Analysis: The dispute centered around whether the provisions of section 40(a)(ia) of the Income Tax Act could be applied in the case of short TDS deduction. The ITAT concluded that it could not, citing a previous judgment by the Gujarat High Court in the case of CIT Vs. Prayas Engineering Ltd. The ruling observed that the Assessing Officer (AO) had completed the necessary verifications in the original assessment, which the PCIT claimed was erroneous and prejudicial to the interest of revenue. Furthermore, the ITAT emphasized that the AO’s initial assessment could not be deemed erroneous, as it was based on adequate scrutiny and application of mind. Conclusion: This landmark verdict underscores the intricate nuances of the Income Tax Act and how they are interpreted and applied. The ITAT’s decision serves as an important reference for future disputes concerning short TDS deduction and the applicability of section 40(a)(ia) of the Act. It reiterates the significance of due diligence by AOs in conducting their assessments and reinforces that shortfalls in TDS deductions should not invoke section 40(a)(ia).
ITR Due Date Extension for Tax Audit Case Not Applicable to Assessee Liable for Audit under Other Acts. Gulu Hassanand Raney Vs Asst. Director of I.T. Bangalore-CPC (ITAT Mumbai)
In the case of Gulu Hassanand Raney vs. Asst. Director of I.T. Bangalore-CPC (ITAT Mumbai), an appeal was filed against the order of assessment passed by the Assistant Director of I.T. The main issue in the appeal was whether the due date for filing the income tax return could be extended for the appellant, who was liable for audit under a law other than the Income Tax Act.
Analysis: The appellant argued that their accounts were audited by qualified chartered accountants as prescribed by the Companies Act, and therefore, the disallowance of the carry forward of business loss was incorrect. They also claimed that they were eligible for the extended due date for filing the income tax return, as they were liable to get their accounts audited as per the RBI’s approval letter. The ITAT examined the relevant documents and noted that the appellant’s accounts were required to be audited under a law other than the Income Tax Act. Based on their interpretation of the law, the ITAT concluded that the due date for filing the income tax return was not extended for the appellant. Consequently, the appellant was not entitled to carry forward the business loss.
Conclusion: The ITAT dismissed the appeal, upholding the order of the Commissioner of Income Tax (Appeals) and the Assistant Director of I.T. The decision clarified that the extended due date for tax audit cases under the Income Tax Act does not apply to assessees liable for audit under other laws.This case highlights the importance of understanding the specific provisions related to the due date for filing income tax returns based on the applicable audit requirements.
Section 44AB: No Audit Required for Assessee not maintaining Books of Account. Bandenawaz Mulla Vs ACIT (ITAT Bangalore)
Introduction: The case involves Bandenawaz Mulla, who filed a return of income for Assessment Year 2017-18 without maintaining books of account. The assessing officer (AO) imposed a penalty under section 271B of the Income Tax Act for the assessee’s failure to get the books audited. The case was appealed to the Income Tax Appellate Tribunal (ITAT) Bangalore. Analysis: The ITAT Bangalore considered the fact that the assessee had not maintained books of account, making it unnecessary to conduct an audit under section 44AB of the Income Tax Act. The ITAT concluded that since there were no books of account to audit, there was no basis for imposing a penalty under section 271B for failure to get the books audited. The ITAT referred to the judgment of the Allahabad High Court in CIT vs. S.K. Gupta & Company, which supported their view.
Conclusion: The ITAT Bangalore allowed the appeal filed by Bandenawaz Mulla and deleted the penalty imposed under section 271B of the Income Tax Act. The ITAT held that when an assessee does not maintain books of account, there is no requirement for an audit under section 44AB, and therefore, no penalty can be levied under section 271B for failure to get the books audited. The decision is in line with the judgment of the Allahabad High Court in CIT vs. S.K. Gupta & Company.
INCOME TAX CIRCULARS & NOTIFICATIONSCompiled by CA. Aloke R. Singh |
|
Income Tax Circulars
| Circular
No |
Date of Issue | Subject |
| 12/2023 | 12/07/2023 | Clarification regarding taxability of income earned by a non-resident investor from off-shore investments in investment fund routed through an Alternative Investment Fund |
| 13/2023 | 26/06/2023 | Condonation of delay under clause (b) of sub-section (2) of section 119 of the Income-tax Act, 1961 for returns of income claiming deduction u/s 80P of the Act for various assessment years from AY 2018-19 to AY 2022-23 |
| 14/2023 | 27/07/2023 | Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for making application for recomputation of total income of a co-operative society engaged in the business of manufacture of sugar, as provided for in sub-section (19) of Section 155 of the Income-tax Act, 1961 |
Income Tax Notifications
| Notification No | Date of Issue | Subject |
| 47/2023 | 06/07/2023 | The CBDT makes amendments in the notification no. 70/2014 dated 13.11.2014, as specified in this notification |
| 48/2023 | 11/07/2023 | For the purpose of section 10(46) of the Income-tax Act, 1961, the Central Government notifies the ‘Yamuna Expressway Industrial Development Authority’, (PAN AAALT0341D), an authority constituted by the State Government of Uttar Pradesh, in respect of the specified income arising to the Authority, as specified in this notification. |
| 49/2023 | 14/06/2023 | The CBDT makes amendments in the notification no. 55/2019 dated 26.07.2019, as specified in this notification. |
| 50/2023 | 17/07/2023 | Income-tax (12th Amendment) Rules, 2023 notified, making substitution in, sub-rule (1) of rule 21AK, clause (a) in Explanation to rule 114AAB and form 10CCF in principal rules in Appendix II. |
| 51/2023 | 18/07/2023 | Income-tax (13th Amendment) Rules, 2023 notified, making amendments in rule 11UAC. |
| 52/2023 | 20/07/2023 | The Central Government specifies that no deduction of income tax shall be made under section 194 of the Income-tax Act from any income in the nature of dividend paid by any unit of an International Financial Services Centre, primarily engaged in the business of leasing of an aircraft (hereinafter referred as payer) to a company, being a Unit of an International Financial Services Centre primarily engaged in the business of leasing of an aircraft (hereinafter referred as payee) subject to the conditions given in this notification. |
| 53/2023 | 21/06/2023 | Corrigendum to notification no. 37/2023 dated 12.06.2023. |
| 54/2023 | 01/08/2023 | Income-tax (14th Amendment) Rules, 2023 notified, inserting rule 6A BBB after rule 6ABBA. |
| 55/2023 | 01/08/2023 | For the purpose of section 10(46) of the Income-tax Act, 1961, the Central Government notifies the ‘Joint Electricity Regulatory Commission (for the State of Goa and Union Territories except Delhi), Gurugram (PAN: AAAJJ0668D), a commission constituted by the Government of India, in respect of the specified income arising to the Commission, as specified in this notification. |
| 56/2023 | 01/08/2023 | The Central Government specifies the bond with the particulars, as specified in this notification, as zero coupon bond for the purposes of the said clause (48) of section 2 of the Income Tax Act, 1961. |
| 57/2023 | 01/08/2023 | The Central Government specifies that no deduction of tax shall be made under section 194-I on payment in the nature of lease rent or supplemental lease rent, made by a person (hereinafter referred as ‘lessee’) to a person being a Unit of an International Financial Services Centre (hereinafter referred as ‘lessor’) for lease of a ship subject to the conditions as specified in this notification. |
DGFT & CUSTOMS UPDATEBy CA. Ashit K. Shah |
|
- Notifications issued under Customs Tariff:
Notifications No Remark Date 44/2023 –
45/2023
Customs
Levy of concessional Basic Custom Duty (BCD) on Liquified Propane and Liquified Butane classified under Chapter 27111200 and 27111300 will have a duty of 2.5% from 1st July 2023. Levy of Agriculture Infrastructure and Development Cess (AIDC) @ 15% is also levied on the import of Liquified Propane and Liquified Butane covered under Chapter 2711 19 10, 2711 19 20 and 2711 19 90 with effect from 1st July 2023.
It is provided that AIDC will not be applicable when such imports are done by Indian Oil Corporation Limited (IOC), Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited (HPCL) or Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited (BPCL) for supply to household domestic consumer or to Non-domestic exempted category (NDEC) customers
01-07-2023 17/2023
–
DGFT
Amendment in the import policy of Fresh (green) Aerca. Import of 17,000 Metric Tonnes of Fresh (green) Aerca covered under HSN 08028010 without a Minimum Import Price (MIP) condition from Bhutan shall be allowed from LCS Jaigaon (INJIGB) and also from LCS Chamurchi (INCHMB) only. Further, import shall be valid subject to a valid port- specific registration certificate issued by DGFT. 03-07-2023 16/2023
–
DGFT
Amendment in the import policy of Potato covered under HSN 07019000 is allowed from Bhutan without any Import License up to 30th June, 2023 is now extended up to 30th June, 2024. 03-07-2023 19/2023
–
DGFT
Amendment in the import policy of Gold covered under HSN 7113 19 11, 7113 19 19 and 7114 19 10 has been amended from “Free” to “Restricted” with effect from 12th July 2023. However, it is further provided that import under HSN 7113 19 11 shall be permitted freely without any import license under a valid INDIA – UAE – CEPA TRQ. 12-07-2023 20/2023 –
DGFTAmendment in export policy of non-basmati rice covered under HSN 1006 30 90 (white rice, semi-milled or wholly milled rice, whether or not polished or glazed) is amended from “Free” to “Prohibited” from 20th July, 2023.The provisions as under Para 1.05 of the FTP 2023 regarding transitional arrangement shall not be applicable under this Notification for export of Non-basmati rice. Consignments of Non-basmati rice will be subject to certain conditions. 20-07-2023 21/2023
–
DGFT
Amendment in export policy of De-oiled Rice Bran covered under HSN 2306 other than those heading 2304 & 2305 is amended from “Free” to “Prohibited” with effect from 28th July 2023 up to 30th November 2023. 28-07-2023 22/2023
–
DGFT
Amendment in export policy of Food supplements containing botanicals covered under HSN 1302 is amended from “Free” to “conditional” whereby exports to European Union (EU) and United Kingdom (UK) originating in or consigned from India and intended for human or animal consumption, allowed subject to issuance of the official certificate issued by Export Inspection Council (EIC) / Export Inspection Agency (EIA), the designated Competent Authority for issuance of official certificate. 31-07-2023
| FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES OF FINANCE Compiled By By Mr. Tushar P. Joshi |
|
There are EIGHT fundamental principles that govern the science of wealth management. If we violate these principles, then the result could be one of the two mentioned below:
- Wealth that we have acquired will disappearOR
- Will put us in distress even it is available adequately.
Like the 8 directions in a compass, these principles help us to navigate in the sea of our life.
These principles have evolved over a few centuries and some of these principles are as old as the history of money is (more than 3000 years).u have that kind of cash with you always? You may even incur more expenses than that. This is where mediclaim comes in. Mediclaim policies or Health Insurance will save you from these sudden shocks in life.
Eight Governing Principles:
- If a person adopts the formula “Income – Expenses = Savings” then he can never become wealthy. The correct formula is “Income – Savings = Expenses!
- Regularity is the key to wealth. (The key to wealth is not the ROI, IRR, CAGR etc.)
- Start early and reach safely.
- Gold and greed can never stay together.
- Purpose must decide the choice.
- Financial Pyramid.
- Draw the map before you start the journey.
- Professional support helps.
Let me explain the first principle here:
Income – Expenses = Savings is not a correct approach. Ironically, you will find a majority of the people on Earth following this approach and all the while aspiring to become rich and wealthy. This formula does not work in real life.
2000 years before one saint called Thiruvaluvar wrote:
“Even if the income were to be small in volume, it is not a matter of concern as long as the expenses are contained within the income.”
This means the secret of wealth management is not in income management but the secret lies in outgo management.
Prof. Adam Smith who is considered to be the father of modern economics says.
“Capitals are increased by Parsimony and diminished by prodigality and misconduct. Whenever a person saves from his revenue he adds to his capital”
All these words of wisdom guides us that we must exercise control over our expenses. These words do not indicate that we must behave like a miser and deprive ourselves of the essentials in order to make wealth, but they only guide us to be sensitive about our expenses and spend on necessities.
We have seen Big companies collapsing when they have not exercised control over their outgo. We have seen airlines companies which have shut down, not because they have engaged people with high salaries and spent lavishly on themselves. We have seen Entertainment companies which started of with a big bang, with star power backing, collapsing under the burden of debts. The same can happen to individuals and families who do not exercise caution in spending.
How to control expenses?
The simplest and the surest method is to make limited money available for that. From our income if we save first for our future, even a small money, we are restricting the money available for our current expenditure.
Spending is for today’s man, savings is for the tomorrow’s man. Out of my earning I must provide for two people 1) Present Tushar Joshi and 2) Future Tushar Joshi. Future Tushar Joshi should not be left solely at the mercy of Future Tushar’s income.
I request each one must follow the above principles which will save their future.

OUR PUBLICATIONS AVAILABLE FOR SALE
| Sr. No. | Name | Price ₹ |
| 1 | FMCG & Pharmaceutical Industry – GST Issues & Challenges | 150/- |
| 2 | Transitional Provision | 50/- |
| 3 | 46th RRC Book | 175/- |
| 4 | Referencer 2023-24 | 750/- |
| 5 | Mega Full Day Seminar Booklet 2.7.2022 | 130/- |
| 6 | Half Day Seminar Booklet 17.11.2022 | 100/- |
| 7 | Maharashtra Goods & Service Tax Act along with Rules (MGST Bare Act) | 850/- |
| 8 | Short Publication GST practical guides (5 Book Series) | 555/- |
| 9 | 47th RRC Book | 250/- |
Payment Link for Publication on sale : https://www.gstpam.org/online/purchase-publication.php
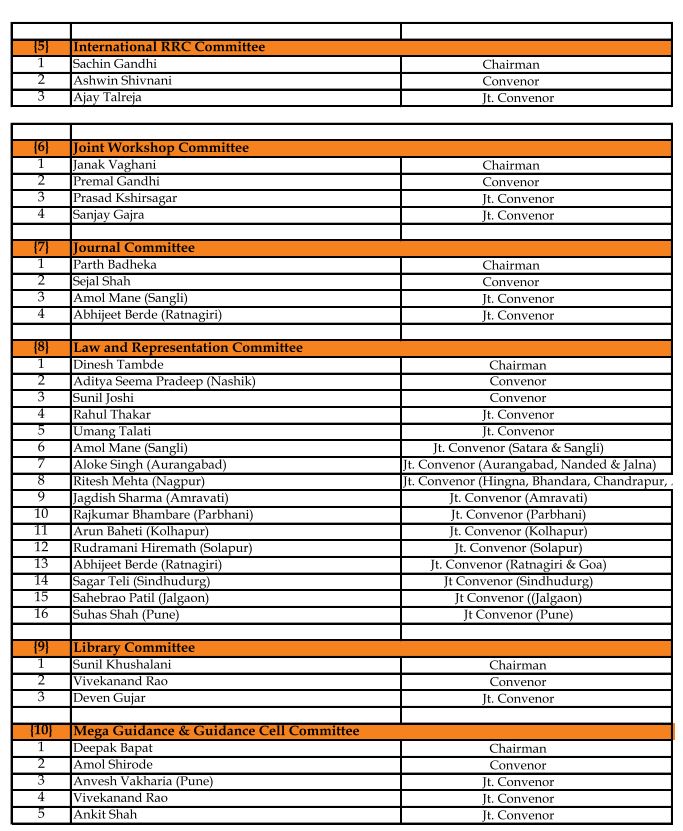
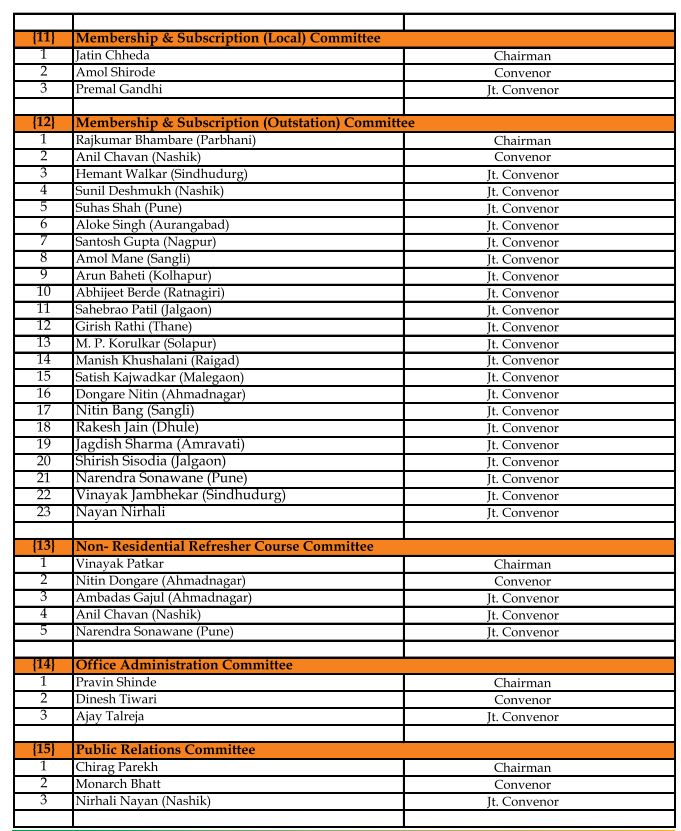
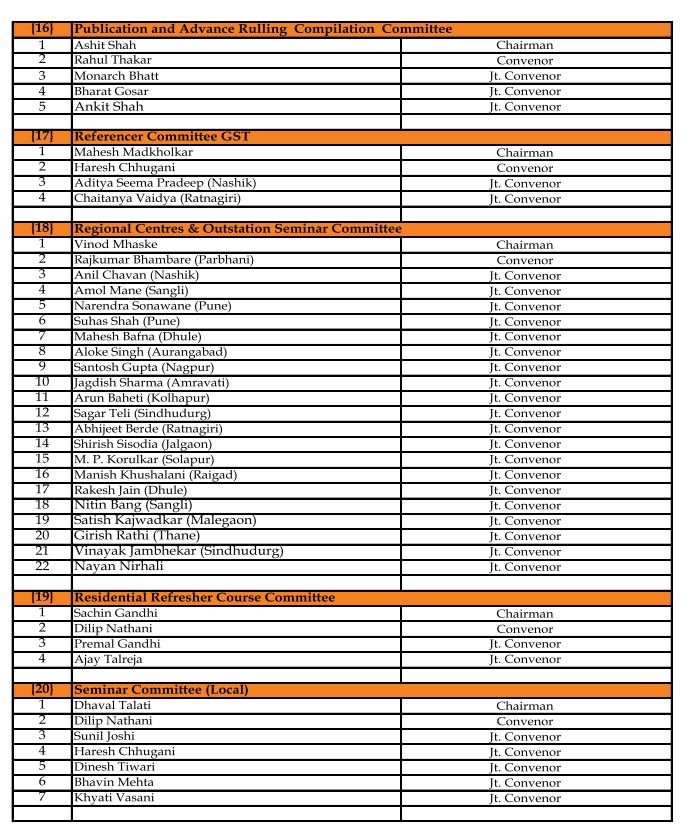
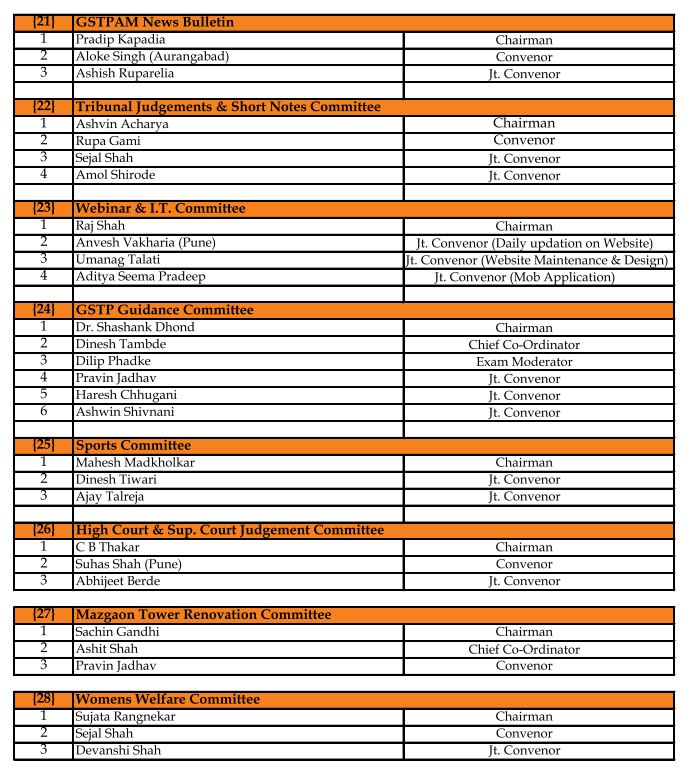
GSTPAM News Bulletin Committee for Year 2023-24
 Pradip Kapadia Chairman |
 Aloke R. Singh Jt. Convenor |
 Ashish Ruparelia Jt. Convenor |






