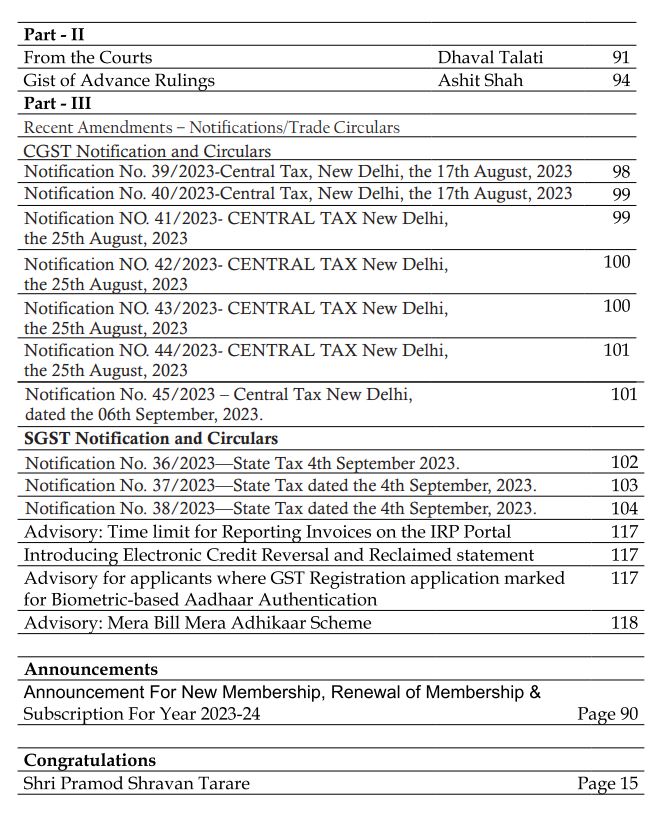
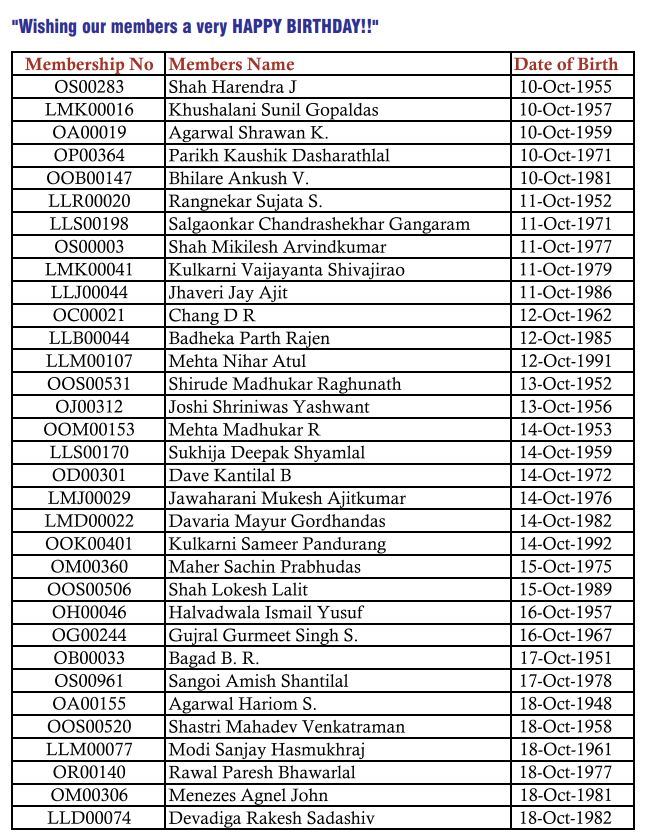
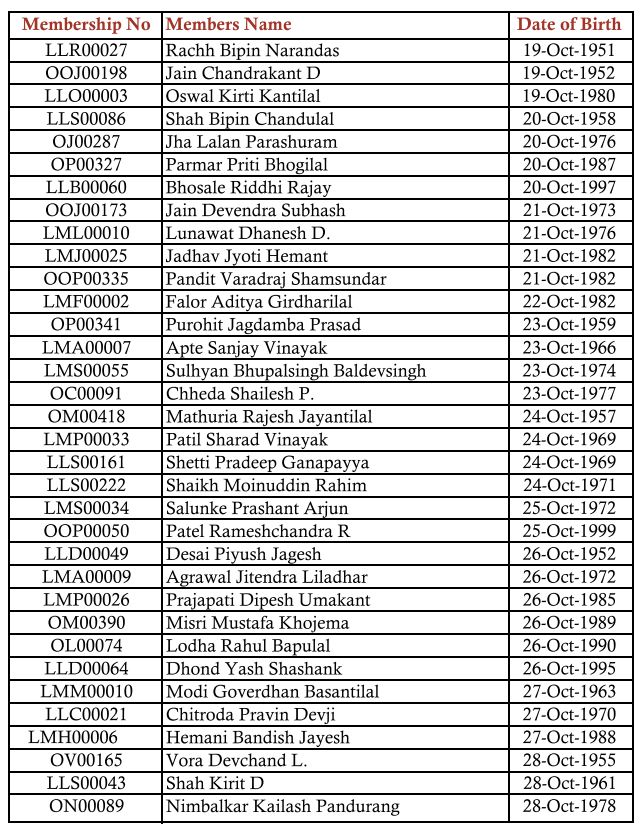
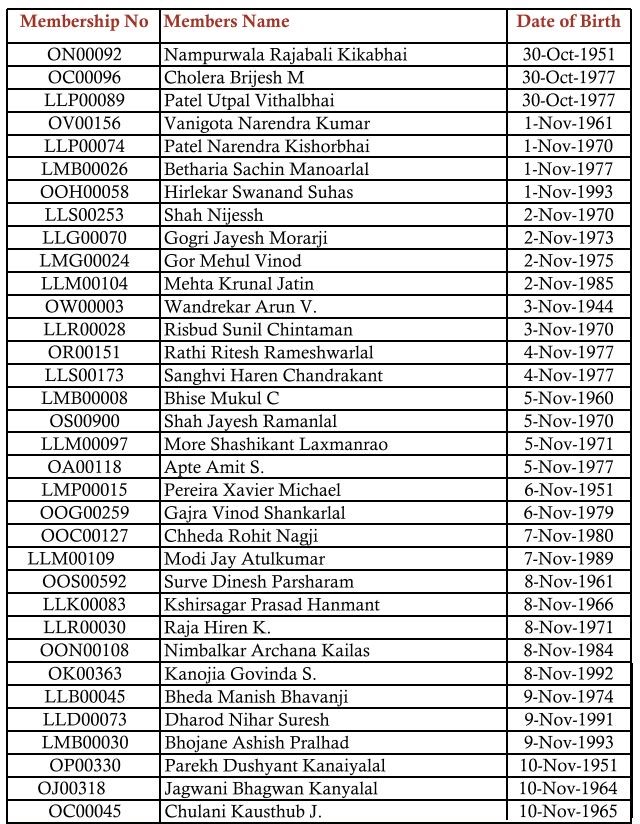
GSTPAM News Bulletin October 2023





GST, MVAT & ALLIED LAW UPDATESCompiled by Adv. Pravin Shinde |
|
| Notification under Central Tax | ||
| Notification No. | Date of Issue | Subject |
| 46/2023-Central Tax | 18.09.2023 | Seeks to appoint common adjudicating authority in respect of show cause notice issued in favour of M/s Inkuat Infrasol Pvt. Ltd. |
| 47/2023-Central Tax | 25.09.2023 | Seeks to amend Notification No. 30/2023-CT dated 31st July, 2023 |
| 48/2023-Central Tax | 29.09.2023 | Seeks to notify the provisions of the Central Goods and Services Tax (Amendment) Act, 2023 |
| 49/2023-Central Tax | 29.09.2023 | Seeks to notify supply of online money gaming, supply of online gaming other than online money gaming and supply of actionable claims in casinos under section 15(5) of CGST Act |
| 50/2023-Central Tax | 29.09.2023 | Seeks to amend Notification No. 66/2017-Central Tax dated 15.11.2017 to exclude specified actionable claims |
| 51/2023-Central Tax | 29.09.2023 | Seeks to make amendments (Third Amendment, 2023) to the CGST Rules, 2017 in supersession of Notification No. 45/2023 dated 06.09.2023 |
| Notification under Central Tax (Rate) |
||
| Notification No. | Date of Issue | Subject |
| 11/2023-Central Tax (Rate) | 29.09.2023 | Seeks to amend Notification No 01/2017- Central Tax (Rate) dated 28.06.2017. |
|
Notification under Integrated Tax |
||
| Notification No. | Date of Issue | Subject |
| 02/2023- Integrated Tax | 29.09.2023 | Seeks to notify the provisions of the Integrated Goods and Services Tax (Amendment) Act, 2023 |
| 03/2023- Integrated Tax | 29.09.2023 | Seeks to notify the supply of online money gaming as the supply of goods on import of which, integrated tax shall be levied and collected under sub-section (1) of section 5 of the Integrated Goods and Services Tax Act,2017 |
| 04/2023- Integrated Tax | 29.09.2023 | Seeks to provide Simplified registration Scheme for overseas supplier of online money gaming |
|
Notification under Integrated Tax (Rate) |
||
| Notification No. | Date of Issue | Subject |
| 11/2023- Integrated Tax (Rate) | 26.09.2023 | Seeks to amend notification No. 8/2017- Integrated Tax (Rate) dated 28.06.2017 to implement decisions of the 50th GST Council. |
| 12/2023-Integrated Tax (Rate) | 26.09.2023 | Seeks to amend notification No. 09/2017- Integrated Tax (Rate) dated 28.06.2017 to implement decisions of the 50th GST Council. |
| 13/2023-Integrated Tax (Rate) | 26.09.2023 | Seeks to amend notification No. 10/2017- Integrated Tax (Rate) dated 28.06.2017 to implement decisions of the 50th GST Council. |
| 14/2023-Integrated Tax (Rate) | 26.09.2023 | Seeks to amend Notification No 01/2017- Integrated Tax (Rate) dated 28.06.2017. |
|
Notification under Union TerritoryTax (Rate) |
||
| Notification No. | Date of Issue | Subject |
| MAHARASHTRA ORDINANCE No. VII OF 2023. Dated 26th September 2023 (English) | 27.09.2023 | Maharashtra Goods and Services Tax (Amendment) Ordinance 2023, (Mah. Ordinance No VII of 2023) (English) |
| MAHARASHTRA ORDINANCE No. VII OF 2023. Dated 26th September 2023 (Marathi) | 27.09.2023 | Maharashtra Goods and Services Tax (Amendment) Ordinance 2023, (Mah. Ordinance No VII of 2023) (Marathi) |
|
Notification / Circular Under MGST Act |
||
| GST Content Category | Date of Issue | Subject |
| 10/2023-Union Territory Tax (Rate) | 26.09.2023 | Seeks to amend No. 26/2018- Union Territory Tax (Rate) to implement the decisions of 50th GST Council. |
| 11/2023-Union Territory Tax (Rate) | 29.09.2023 | Seeks to amend Notification No 01/2017- Union territory Tax (Rate) dated 28.06.2017. |
| SUMMARY OF RECENT CASES UNDER GST
Compiled by CA Aditya Surte |
|
- Composite supply of services to Food and Supplies Department of State Government by way of milling of whole wheat grains provided by State Government, its fortification and packing for distribution under Public Distribution System is eligible for exemption, since value of goods involved in such composite supply does not exceed 25 per cent of value of supply.
(West Bengal Authority for Advance Rulings in Order No. Order No. 14/WBAAR/2023-24, decided on 13/07/2023 in the case of Aryan Flour Mills Pvt. Ltd.) - ITC is not blocked on GST paid towards leasing / renting and hiring of motor vehicles for providing transportation facility to women employees working in shifts, arriving or leaving the workplace between 8 pm to 6 am where providing such facility is mandatory as per the Tamil Nadu Shops and Establishment Act, 1947.(Tamil Nadu Advance Ruling Authority in Advance Ruling No. 14/ARA/2023, decided on 15/06/2023 in the case of Access Healthcare Services Pvt. Ltd.)
- Where the Applicant operates ‘Namma Yatri’ App for connecting the supplier of services (auto driver) and recipient (passenger) by charging membership fee and subscription fee (on which GST is paid by the Applicant) but does not collect consideration (auto fare) from the recipient and has no control over actual provision of service by the supplier, the Applicant does not satisfy the conditions of section 9(5) of CGST Act for discharge of tax liability by electronic commerce operator. Applicant merely connects auto driver and passenger, and its role ends on such connection.
(Karnataka Advance Ruling Authority in Advance Ruling No. KAR ADRG 31/2023, decided on 15/09/2023 in the case of Juspay Technologies Pvt. Ltd.) - When raw materials purchased are already used in manufacture of finished goods and finished goods are destroyed in fire accident completely, ITC is required to reversed; when raw materials procured are lost in fire accident before use in manufacture of finished goods, ITC is required to reversed; when destroyed finished goods can be sold as steel scrap in open market and output tax liability on such supply of scrap is paid, ITC is required to reversed.
(Telangana Advance Ruling Authority in Order No. 15 of 2023 in A.R.Com/04 of 2023, decided on 02/09/2023 in the case of Geekay Wires Ltd.)
| GIST OF TRIBUNAL JUDGEMENTS (VAT)
Compiled by CA Rupa Gami |
|
-
- Ortek Computers in Vat Second Appeal No. 99of 2020 Madhav Gems in Vat Second Appeal No. and 10 of 2020M/s P.P. Platopack in Vat Second Appeal No. 42 of 2020 decided on 17/08/2023
In all the above cases returns had been filed claiming refund. Form 501 had not been filed or filed late manually. A simple letter was submitted for processing of refund to the Assessing Officer. The Assessing Officer denied the refund citing the reason that the assessment was time barred and that Form 501 was not filed. On first appeal filed, the same was rejected for the reason that the appeal was filed against the letter issued by the Assessing authority rejecting the request for refund and it was not an order against which appeal could be filed.
The Hon’ble Tribunal relied on the following judgements:- The Supreme Court judgement in the case of Director of Income tax v/s Tata Chemical Ltd. decided on 26/02/2021 where the Court held that “refund due and payable to the assessee is a debt owed and payable by the revenue”
- Vichare and Co. Pvt. Ltd. where the Court held that if the returns are furnished and submitted, they deserve to be scrutinised expeditiously and for which the Department had issued an internal circular no. 3A dated 16/03/2015prescribing the time limit for scrutiny of returns.
- Om Shree Developers decided on 12/10/2021 which relied on the Vichare and Co.
and allowed the appeal and remanded the matter to the Assessing Authority to scrutinise the application for refund and refund the excess amount. (Petitioner represented by Adv. C.B. Thakar)
- Suprajit Engineering Ltd. in Vat Appeal No. 530/2018, Pune Bench decided on 28/08/2023
The appellant made part payment of Rs.2000000/- on filing first appeal. The first appeal order resulted in a refund of Rs.2000000/-. According to the appellant , he was entitled to interest on this refund which was denied by the first appellate authority. The appellant is before the Hon’ble Tribunal on this issue of interest. The Hon’ble Tribunal held that amount paid towards compliance of section 26(6)(B) of MVAT Act is the amount of tax, that part payment is nothing but the quantum of tax paid by the appellant against the disputed amount of tax and the amount resulted in refund in first appeal. Therefore, refund is nothing but refund of amount of tax. The appellant is entitled to interest on the amount of refund of tax under section 52 of the MVAT Act. (Petitioner represented by STP P.G. Joglekar) - M/s Manek Enterprises in Vat S.A. No. 125/126 /2019 Pune Bench decided on 25/08/2023
In this case Penalty u/s 29(4) was levied at a higher amount than the tax amount. First appeal was dismissed. In second appeal, the tribunal allowed the appeal holding that the Commissioner is not allowed to impose the penalty u/s 29(4) of the MVAT Act more than the tax due. (Petitioner represented by Adv. C. B. Thakar) - Orix Auto Infrastructure Services Ltd. in Vat S.A. No.743 of 2017 dated 21/01/2022
The appellant was engaged in the works contract of central installation work of air-conditioning (supply, installation, testing and commissioning of HVAC and electrical work). This work was carried out when the construction of hotel was going on and before the completion of hotel construction work. The appellant had filed returns and paid taxes under composition scheme of section 42(3) at 5% treating it as activity ancillary or incidental to construction contract. The Assessing authority treated it as other works contract and levied tax at 8%. The first appeal was dismissed for non-attendance and restoration of appeal was rejected. The Hon’ble Tribunal held this as work ancillary to the main work of construction and fit to get the benefit of the notification dated 30.11.2006 which defined construction contract and y therefore is taxable at 5%.
Further for vat charged on service tax the Hon’ble Tribunal held that service tax cannot form part of turnover of sales as per the decision in the case of Sujata Painters and for periods prior to 1st April, 2015, the Department has accepted the Tribunal decision.
(Petitioner represented by CA Mr. Lunawat) - Addl. Commr. of Sales Tax, Vat-III, Mumbai vs Bombay Quarries in Rectification Application No.59 of 2016 in SA No. 219 of 2015 dated 19/01/2022
The Assessing authority disallowed claim of ITC due to non-submission of ledger confirmations from some vendors. In first appeal the same was confirmed. In second appeal, the Hon’ble Tribunal was pleased to allow the appeal by giving directions to department to “issue notice to selling dealer of the respondent for production of the confirmation of mismatch purchases.
”The State of Maharashtra filed rectification application against this order to state that there was a mistake in the order of the Tribunal that it had issued directions to issue notices to the vendors of the appellant for mismatch confirmations. The Tribunal observed that in the case of Hon’ble Bombay High Court judgement in the case of Mahalaxmi Cotton, the department had promised the Court that it will make all efforts to recover unpaid tax from the sellers who collected it, which they could not produce any evidence that any efforts were made to verify the correctness of J1 Annexure. The directions of the Tribunal were not illegal directions. The Tribunal held that a mistake apparent on record must be an obvious mistake and not something which can be established by a long drawn process of reasoning. The Rectification Application was dismissed.
(Respondent represented by Adv. D. B. Avhad) - M/s Zaf Enterprises in Vat S.A. No. 107 of 2021 dated 11/01/2022
The first appeal was rejected for non-attendance of the consultant. An application for restoration of appeal was filed and heard. However, the restoration application was rejected. The Tribunal held that the appellant should not suffer due to negligence on the part of the consultant and relying on its own judgement in the case of M/s. M.K. Industrial Suppliers in Misc. App. No. 168 of 2012 in S.A. No. 327 of 2012 set aside the rejection order and restored the appeal.
(Petitioner represented by Adv. C.B.Thakar) - Orix Auto Infrastructure Services Ltd. in Vat S.A. No.743 of 2017 dated 21/01/2022
The period being 2007-08 when Vat Audit Form was not electronic and Annexure J1 and J2 statement was not available on automated system of MGSTD, Trade Circular 22T of 2010 was issued whereby duty was cast on the Department to carry out the verification at the vendors place to find out if the vendors had paid the taxes. In the present case the FAA had not been able to discharge this burden. However, the appellant had obtained the ledger confirmations on his own which covered more than 50% of the set off claim. The Tribunal set aside the appeal order with a direction to allow the ITC if it was not from non genuine dealers or RC cancelled tax payers.
- Ortek Computers in Vat Second Appeal No. 99of 2020 Madhav Gems in Vat Second Appeal No. and 10 of 2020M/s P.P. Platopack in Vat Second Appeal No. 42 of 2020 decided on 17/08/2023
(Petitioner represented by CA Sujata Rangnekar)
INCOME TAX UPDATESCompiled By By Adv. Ajay Talreja |
|
Tax Treatment of Agricultural Land Sale: No Need for Active Agricultural Activity
Case Name : ACIT Vs Ashok W. Wesavkar (ITAT Mumbai)
Appeal Number : I.T.A. No. 5147/Mum/2017
Date of Judgement/Order : 02/05/2023
Related Assessment Year : 2011-12
Courts : All ITAT
In this case of ACIT vs. Ashok W. Wesavkar, the issue revolved around the tax treatment of the sale of agricultural land by the assessee. The assessee, who was a professional architect, had sold agricultural lands to Mayank Land Pvt. Ltd. for a considerable sum. The assessee claimed that the sale of agricultural land was not liable for capital gains tax as it did not qualify as a capital asset. The Assessing Officer denied the exemption and asserted that the assessee had not carried out agricultural activities on the land, and thus, the income was not offered for taxation as agricultural income in the income tax return. The Assessing Officer relied on a report by an Inspector stating that the land was not suitable for agricultural activity. Upon appeal, the CIT(A) called for a remand report and examined the assessee under section 131 of the Income Tax Act. After considering the assessee’s contentions and evidence, the CIT(A) allowed the claim, stating that the sale consideration was not liable to be taxed as capital gains. However, when the Revenue appealed the decision, there was a difference of opinion among the members of the Income Tax Appellate Tribunal (ITAT). As a result, the matter was referred to a Third Member. The Honourable Third Member examined various case laws on the subject and explained the law regarding the sale of agricultural land. The key point considered was that the land in question was shown as “Lagavadi Yogya Sherta” (Cultivable land) in the land revenue record. The assessee had also grown vegetables and minor millets on the land, which further supported its agricultural nature. The location of the land was in Raigad District. The Honourable Third Member highlighted that Section 2(14)(iii) of the Income Tax Act does not prescribe any condition that active agricultural activity must be present at the time of land sale. The only requirement is that the land should qualify as agricultural land.
ITAT: Assessment Order without DIN, Breaching CBDT Circular, is Invalid
Prabhakar Amruta Shillak Vs ITO (ITAT Pune)
The Income Tax Appellate Tribunal (ITAT) Pune dealt with an appeal filed by Prabhakar Amruta Shillak against the order of the National Faceless Appeal Centre (NFAC) for the assessment year 2012-13. The appellant challenged the addition made to the income under Section 69A of the Income Tax Act, 1961. However, during the physical hearing, a new legal ground was raised, challenging the validity of the assessment order itself. The appellant contended that the assessment order was invalid as it did not comply with the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) Circular No.19/2019, which mandated the generation and communication of a Document Identification Number (DIN) for all official communications. The circular came into effect from October 1, 2019. The assessment order was passed on October 30, 2019, and the appellant argued that the absence of DIN in the order rendered it invalid. The ITAT accepted the legal ground raised by the appellant and held that the assessment order was invalid due to the non-compliance with the CBDT circular. The failure to generate and quote DIN in the order resulted in it being treated as never issued, rendering it ineffective in the eyes of the law. As a result, the ITAT did not delve into the merits of allowed the appeal in favor of the appellant.
How to file past years ITR for VISA application?
Sometimes, we do not file ITR within the due date & often ITR of few past years are missed due to various reasons. If you are planning to apply for VISA, it generally requires ITRs of past 2-3 years as a part of documentation required for VISA application. Since we have missed filing the ITR, it becomes pertinent for us to get the ITR filed for past years. The income tax act has specified certain time limits & due dates, within which ITR for a particular year must be filed. For instance, the due date for regular ITR for Individuals was 31st July 2023 for AY 2023-24. So, if one has missed this due date, they can no longer file the regular ITR. However, a belated ITR for AY 2023-24 can be filed up to 31st December 2023 by paying late fees as applicable which depends upon the taxable income. The objective of this article is to provide the way-out for the missed ITR of previous assessment years and a few past years as well, which might be required for VISA application of various countries.
Can we file ITR of any number of past years?
ITR for any number of past years cannot be filed. There are 2 options by which one can file the missed ITR: Filing belated ITR – This can be filed up to 31st December of the ongoing year. So, belated ITR for FY 2022- 23 can be filed up to 31st December, 2023 Filing updated ITR through ITR U- This could be used to file ITR of past years, subject to certain conditions. Currently, ITR for FY 20-21 & 21-22 can be filed through ITR U and if one requires to file ITR for FY 22-23 after 31st December 2023, it will be done through ITR U.
What is the time limit for filing ITR through ITR U?
ITR U allows filing the ITR up to the end of 24 months from the end of relevant assessment years. So, ITR for FY 20-21 can be filed up to 31st March 2024, for FY 21-22, it can be filed up to 31st March 2025 and ITR of FY 22-23 can be filed up to 31st March 2026 & so on
Can ITR U be filed freely & under all situations or are there any conditions/situation under which ITR U can be used?
There are specified situations under which ITR U can be used and it also comes with certain conditions which must be satisfied to file the ITR.
Purchases reflected in books can’t be treated as unexplained investment Vimal Kishor Shah Vs ITO (ITAT Mumbai)
Introduction: In the case of Vimal Kishor Shah vs ITO, ITAT Mumbai was faced with a pivotal issue regarding the treatment of certain purchases as unexplained investments. The appeals filed by the assessee were in response to orders passed by the learned CIT(A) for the A.Y. 2011-12 & 2014-15, wherein purchases of jewellery and shares were under scrutiny. This ruling represents an essential development in how financial transactions and investments are assessed under Indian tax law.
Analysis: The core of this dispute involves two significant points: purchases of jewellery treated as unexplained investments under section 69 of the Act, and the assessment of sale value of shares as unexplained cash credit under section 68 of the Act.
- Unexplained Investment in Jewellery: The assessee purchased jewellery from two concerns belonging to the Rajendra Jain Group. Even though the payment was made through a banking channel and reflected in the books of accounts, the Assessing Officer treated them as unexplained investments. ITAT found merit in the assessee’s argument, setting aside the CIT(A)’s order.
- Sale Value of Shares as Unexplained Cash Credit: The Assessing Officer considered the sale consideration of shares as bogus, treating the sale value as taxable income under section 68. ITAT observed that the assessee was a regular investor, had held the shares for over two years, and that the increase in share price was normal in the market. Consequently, they set aside the order assessing the sale consideration as unexplained cash credit.
Conclusion: The decision of ITAT Mumbai in the case of Vimal Kishor Shah vs ITO is emblematic of the critical necessity for clear evidentiary procedures and rational assessment in tax proceedings. By acknowledging that purchases made through proper channels and duly reflected in the books cannot be treated as unexplained investments, the ruling underscores the importance of transparency and fairness in tax administration. Both the appeals filed by the assessee were allowed, setting an important precedent in the treatment of investments under Indian tax laws.
Income Once Taxed as House Property Can’t Be Stray-Taxed as Business Income Later
ACIT Vs International Recreation Parks (P) Ltd (ITAT Delhi)
The Income Tax Appellate Tribunal (ITAT) in Delhi recently delivered a verdict in the case between the Assistant Commissioner of Income Tax (ACIT) and International Recreation Parks (P) Ltd. The crux of the matter revolves around the proper classification of income—specifically, whether income once taxed as house property can later be re-classified and taxed as business income. This case has generated considerable interest among tax experts, property developers, and businesses alike.
The Case Background:- The assessee, International Recreation Parks, was allotted land for 90 years by the Noida Authority, primarily for developing an amusement park. The company claimed that its income was from development for amusement park purposes, including signage, kiosks, and maintenance services. This income had been classified as income from house property in previous assessments, and the authorities had accepted this classification.
The Controversy:– The issue arose when the Assessing Officer (AO) noted that the primary revenue of the company was from letting out commercial complexes. The AO then moved to classify this income as business income, deviating from earlier classifications. This move was contested and eventually overturned by the CIT(A), who upheld the assessee’s original classification. Legal Insights The CIT(A) referenced the Hon’ble Supreme Court’s decision in the case of Raj Dadarkar & Associates Vs. ACIT. In this case, it was determined that income from sub-licenses should be taxed as income from house property, not as business income.
Consistency Matters The CIT(A) also pointed out the principle of consistency. When a head of income has been accepted in the preceding and subsequent years’ assessments, then changing it for a particular year without compelling reasons is unjustifiable.
Conclusion :-
The ITAT Delhi, affirming the CIT(A)’s verdict, clarified that while the principle of res judicata may not apply to income tax proceedings, the principle of consistency should not be overlooked. In this case, since the revenue had accepted the income as house property in preceding and subsequent years, changing the classification was unwarranted. Therefore, this ruling reiterates the importance of consistency in tax assessments and serves as a crucial reference for future tax disputes involving the classification of income.
DGFT & CUSTOMS UPDATEBy CA. Ashit K. Shah |
|
1. Notifications issued under Customs Tariff:
| Notifications No | Remark | Date |
| 52/2023
– Customs |
Amendment in the existing exemption Notification No. 50/2017 whereby exemptions provided to textile machineries in S. No. 460 has been now extended to shuttleless rapier looms, shuttleless waterjet looms, and shuttleless airjet looms with specific speed thresholds. Additionally, parts and components used in the manufacturing of shuttleless looms are included within this revised ambit. Moreover, exemptions of these benefits will be valid only up to 31st March 2025 and beyond this date exemption ceases to be effective. | 05-09-2023 |
| 53/2023
– Customs |
Basic Customs Duty (BCD) on select items such as apples, almonds, lentils and chikpeas imported from the US. Duty on lentils imported from the US has now been fully exempted, which was earlier 20%. Similarly, import duty on almond has been lowered to 35% from 41% earlier. In the case of apples, the duty has been lowered to 15% from the earlier 35%. In the case of chikpeas, an import duty of 10% will be applicable at par with imports from other nations. | 05-09-2023 |
| 55/2023
– Customs |
Amendment in the entries relating to Phased Manufacturing Program (PMP) for wearable devices (Wrist Wearable Devices commonly known as smart watches falling under HSN 8517 62 90 and its inputs / parts / sub parts and Hearable devices and its inputs / parts / sub parts in the N. No. 11/2022 and 12/2022. | 14 -09-2023 |
| 56/2023
– Customs |
Exemption from BCD and IGST on specified military equipment, if imported by Ministry of Defense, or Defense Forces, or the Defense Public Sector Units or other Public Sector Units or any other entity. Now, such exemption is also extended to parts, machinery and technical documentation required for the manufacturing of AK-203 rifles. | 15-09-2023 |
| 57/2023
– Customs |
Exemption of Export Duty on export of Bangalore Rose Onion subject to condition that exporter furnishing a certificate from the Horticulture Commissioner, Government of Karnataka, certifying the item and quantity of Bangalore Rose Onion to be exported. Prior to amendment 40% duty was levied on export of onions. | 29-09-2023 |
| 70/2023
– Customs (NT) |
Exemptions from deposits in to Electronic Cash Ledger under Customs Act in respect of specified goods under section 51 (4) of the Customs Act, 1962, until 1st December, 2023.
This extension of exemption applies to: I. Goods imported or exported in customs stations where customs automated systems are not in place. II. Accompanied baggage. III. Deposits other than those used for making payment of: (a) Any duty of customs, including cesses and surcharges levied as duties of customs. (b) Integrated tax. © Goods and Service Tax Compensation Cess. (d) Interest, penalty, fees, or any other amount payable under the said Act, or the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 (51 of 1975). |
27-09-2023 |
| 09/2023
– Customs (Add) |
Continuation of levy of Anti-Dumping Duty (ADD) on import of Flat Base Steel Wheels covered under chapter 8708 70, originating in, or exported from China PR, and imported in to India for a period of 5 years. | 11-09-2023 |
| 08/2023
– Customs (Add) |
Levy of Anti-Dumping Duty (ADD) on import of “Fishing Net” covered under chapter 5608 11 10, originating in, or exported from China PR & Malaysia and imported in to India. | 29 -08-2023 |
| 33/2023
– DGFT |
The existing rates for all the items covered under RoDTEP will be applicable for exports made from 01.10.2023 to 30.06.2024. However, it would be subject to the budgetary framework as provided under Para 4.54 of FTP 2023 so that the remissions for current financial year are managed within the approved Budget of the Scheme. | 26 -09 -2023 |
| 25/2023
– DGFT |
Pre-shipment and Post-shipment Export Credit and Packing Credit in Foreign Currency (PCFC) for E-Commerce Exports to be provided by Banking and Financial Institutions based on the extent guidelines issued by RBI. | 04 -09 -2023 |
| 23/2023
– DGFT |
Clarification provided in respect of implementation of the Trade Notice No. 07/2023-24 dated 08.06.2023 in reference to the pre-import condition under Advance Authorisation Scheme for all imports made on or after 13-10-2017 and up to and including 09-01-2019 which could not meet the “pre-import condition” may be regularized by making payment of fees. | 03 -08 -2023 |
CHARITABLE TRUSTS UPDATESBy Adv. Hemant Gandhi & CA Premal Gandhi |
|
Extension of due date to submit Audit Report in Form no. 10B/10BB and ITR-7
The CBDT has extended the following due dates:
-
- The due date for submission of audit report in Form 10B/10BB for entities registered under section 10(23C) and section 12A has been extended from 30th September 2023 to 31st October 2023.
- The due date to file the return of income in ITR-7 for assessment year 2023-24 has been extended from 31st October 2023 to 30th November 2023.
Vide Circular no. 16/2023 dated 18th September,2023.
Extension of FCRA registration up to 30th September 2023
In continuation of the Public Notice dated 24th March 2023, the Ministry of Home Affairs (‘MHA’) has extended the validity of FCRA registration certificates of the following entities:
- entities whose validity was extended till 30th September 2023 and whose renewal application is pending.
- entities whose five-year validity period will expire between 1st October 2023 and 31st March 2024, and they have applied/will apply for renewal before the expiry of five years
The validity of registration of entities falling in either of the above cases is extended up to 31st March 2024 or till the date of disposal of the renewal application, whichever is earlier.
As a natural corollary, such entities will be allowed to receive and utilise the foreign contribution up to 31st March 2024 or till the date of disposal of the renewal application, whichever is earlier.
However, if the application for renewal of registration certificate is rejected, the validity of the certificate shall be deemed to have expired on the date of refusal of the application and the association will not be able to receive or utilise foreign contribution, thereafter.
Vide public Notice no II/21022/23(22)/2020-FCRA-III dated 25th September 2023.
TIPS FOR FINANCIAL GOALSCompiled By By Mr. Tushar P. Joshi |
|
Framing objectives or goals is the first step in financial planning. Here are the important things to keep in mind while doing so.
Set Specific Goals
It is important to set specific financial goals. People tend to assign random figures for their goals without understanding whether the money saved will be sufficient or whether it will be feasible to put away a big amount. A retirement corpus of 2 crore may seem enough at today’s prices, but it may not be enough 20 years from now. Financial planning should not be based on approximations and instinct. Do the math and set specific goals, mentioning the amount you need to save and the time available to achieve each of them.
Prioritise The Goals
Investors often have a haphazard list of goals. However, each goal should be assigned a level of priority, depending on its importance, time horizon, financial impact on other goals, and the manner in which you will arrange the funds for it. For instance, buying health insurance is a more important and immediate need than buying a car. Also, it will ensure that your other goals remain intact since a medical exigency will not wipe out your savings.
Similarly, planning for your retirement takes priority over your child’s college education, simply because you can take a loan for education, but you won’t be able to get one for your sunset years.
Make Small Beginnings
Studies show that the bigger and farther the goal, the less likely that an investor will save for it. If the amount to be saved is too large or the time available is too long, an investor is likely to give up.
Instead of becoming intimidated by the huge amount required to be saved, take baby steps towards that goal. You can scale up the savings later when you have a higher investible surplus. I would advise that one should increase the investment in line with the rise in his income.
Don’t Ignore Inflation
Surprisingly, while people complain about everyday inflation, they ignore the impact it can have on their long- term goals. Even a minor change in the inflation rate will increase expenses manifold while reducing the value of savings. If the cost of your daughter’s higher education is 50 lakh today, even 8% inflation will push up the figure to over 1 crore in 10 years.
Factor in inflation while calculating the amount you require for your goals. This will decide the sum you will need to invest for each goal. To ensure that your financial plan is on track and that your estimates are not off the mark, you should regularly evaluate the plan.
Match Duration With Investment
Every goal has a different time frame. So you need to match the Investment Avenue with the time available for that goal. If you have less than three years to save for your son’s college admission, you should invest in debt rather than equity to ensure the safety of your capital.
“The Secret Of Financial Success Is Getting Started.”


OUR PUBLICATIONS AVAILABLE FOR SALE
| Sr. No. | Name | Price ₹ |
| 1 | FMCG & Pharmaceutical Industry – GST Issues & Challenges | 150/- |
| 2 | Transitional Provision | 50/- |
| 3 | 46th RRC Book | 175/- |
| 4 | Referencer 2022-23 | 375/- |
| 5 | Referencer 2023-24 | 750/- |
| 6 | Mega Full Day Seminar Booklet 2.7.2022 | 130/- |
| 7 | Half Day Seminar Booklet 17.11.2022 | 100/- |
| 8 | Maharashtra Goods & Service Tax Act along with Rules (MGST Bare Act) | 850/- |
| 9 | Short Publication GST practical guides (5 Book Series) | 555/- |
| 10 | 47th RRC Book | 250/- |
Payment Link for Publication on sale : https://www.gstpam.org/online/purchase-publication.php
GSTPAM News Bulletin Committee for Year 2023-24
 Pradip Kapadia Chairman |
 Aloke R. Singh Convenor |
 Ashish Ruparelia Jt. Convenor |








